 Navigating the Corporate Entity Code is essential for any business aiming to establish a robust legal framework and operational structure. In the intricate landscape of corporate law, understanding the principles and practices embedded within the Corporate Entity Code is paramount. This code serves as a foundational guide, delineating the rules and regulations that govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of corporate entities.
Navigating the Corporate Entity Code is essential for any business aiming to establish a robust legal framework and operational structure. In the intricate landscape of corporate law, understanding the principles and practices embedded within the Corporate Entity Code is paramount. This code serves as a foundational guide, delineating the rules and regulations that govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of corporate entities.
At its core, the Corporate Entity Code encapsulates the legal framework through which businesses organize and conduct their affairs. It encompasses a spectrum of entities, ranging from sole proprietorships and partnerships to corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs). Each entity type carries distinct characteristics and obligations, and compliance with the code ensures that businesses operate within the bounds of the law while maximizing their strategic objectives.
Key principles outlined in the Corporate Entity Code encompass various facets of corporate governance, including the allocation of rights and responsibilities among stakeholders, mechanisms for decision-making and accountability, and protocols for corporate transactions and restructuring. Understanding these principles is fundamental for stakeholders, ranging from entrepreneurs and executives to legal advisors and regulators, as they navigate the complexities of corporate affairs.
Moreover, the Corporate Entity Code lays down best practices for corporate compliance and risk management. It delineates requirements for maintaining accurate corporate records, filing periodic reports with regulatory authorities, and adhering to ethical standards in business conduct. By adhering to these practices, businesses not only mitigate legal and financial risks but also enhance their credibility and trustworthiness in the marketplace.
Formation and Structure
- Entity Selection:Understanding the different types of corporate entities available under the Corporate Entity Code, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and LLCs, and selecting the most suitable structure based on factors such as liability protection, tax implications, and management flexibility.
- Incorporation Process:Guiding businesses through the procedures and requirements for incorporating a corporate entity, including filing articles of incorporation, drafting bylaws or operating agreements, and obtaining necessary permits and licenses.
- Capitalization and Ownership:Establishing the framework for capital structure and ownership distribution within the corporate entity, including issuing shares of stock or membership interests, setting forth voting rights and dividend preferences, and structuring equity incentives for key stakeholders.
- Compliance Obligations:Familiarizing businesses with ongoing compliance obligations under the Corporate Entity Code, such as holding annual meetings, maintaining corporate records, and filing periodic reports with regulatory authorities.
- Corporate Governance:Implementing effective corporate governance mechanisms to facilitate decision-making, manage conflicts of interest, and ensure accountability among directors, officers, and shareholders.
Operations and Transactions
- Contractual Relationships:
Advising businesses on entering into contractual agreements and transactions in compliance with the Corporate Entity Code, including negotiating and drafting commercial contracts, licensing agreements, and employment contracts.
- Corporate Finance:
Exploring avenues for raising capital and financing corporate activities, such as issuing debt securities, obtaining bank loans, or seeking venture capital or private equity investment, while adhering to regulatory requirements and fiduciary duties.
- Mergers and Acquisitions:
Guiding structuring of mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures following the Corporate Entity Code, including conducting due diligence, negotiating transaction terms, and obtaining shareholder approval.
- Corporate Restructuring:
Assisting businesses in navigating corporate restructuring initiatives, such as spin-offs, consolidations, or reorganizations, to optimize operational efficiency, strategic focus, or capital allocation.
- Compliance and Risk Management:
Developing comprehensive compliance programs and risk management strategies to mitigate legal, regulatory, and operational risks, including data privacy and cybersecurity compliance, environmental regulations, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Taxation and Financial Reporting
- Tax Planning Strategies:
Delving into tax planning strategies and considerations for corporate entities under the Corporate Entity Code, including optimizing tax efficiency through entity selection, capital structure, and transaction structuring. This section would cover key tax implications for different entity types, such as pass-through taxation for partnerships and LLCs versus corporate taxation for C corporations, as well as discuss tax deductions, credits, and incentives available to businesses.
- Financial Reporting Requirements:
Explaining the financial reporting obligations imposed by the Corporate Entity Code, including preparing and filing financial statements following generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or other applicable accounting standards. This section will cover topics such as annual financial reporting, disclosure requirements for publicly traded companies, and the role of auditors in ensuring financial transparency and accuracy. Additionally, it would address the importance of maintaining proper internal controls and corporate governance practices to enhance financial reporting reliability and integrity.
Corporate Compliance and Ethics
- Regulatory Compliance Framework:
Discussing the regulatory landscape governing corporate conduct and compliance obligations under the Corporate Entity Code, including industry-specific regulations, consumer protection laws, and anti-corruption measures. This section would outline strategies for businesses to stay abreast of regulatory changes, establish compliance programs, and conduct internal audits to ensure adherence to legal requirements and ethical standards.
- Ethical Business Practices:
Emphasizing the importance of ethical business conduct and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives within the framework of the Corporate Entity Code. This section will explore ethical dilemmas faced by corporate entities, such as conflicts of interest, bribery and corruption, environmental sustainability, and employee rights. It would also highlight the role of corporate culture, leadership commitment, and stakeholder engagement in fostering a culture of integrity and ethical decision-making throughout the organization.
Conclusion:
Mastering the Corporate Entity Code is not merely a legal requirement but a strategic imperative for businesses seeking sustainable growth and resilience in today’s dynamic marketplace. By navigating the key principles and practices outlined within this code, organizations can establish a solid foundation for their operations, minimize legal and regulatory risks, and unlock opportunities for innovation and expansion.
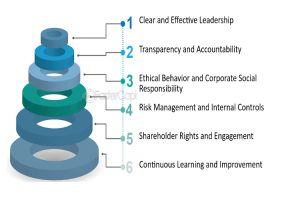
The Corporate Entity Code serves as a roadmap for businesses, guiding them through the complexities of corporate governance, compliance, and strategic decision-making. From the formation of the entity to its daily operations and strategic transactions, adherence to the principles embedded within the code fosters transparency, accountability, and trust among stakeholders.
Moreover, compliance with the Corporate Entity Code is not just about meeting regulatory obligations; it is about upholding ethical standards and corporate values. By prioritizing integrity, transparency, and social responsibility, businesses can build a reputation for trustworthiness and sustainability, enhancing their competitive advantage and fostering long-term relationships with customers, investors, and communities.
As businesses continue to navigate an increasingly interconnected and regulated business environment, understanding and adhering to the Corporate Entity Code will remain essential. By embracing the principles and practices outlined within this code, businesses can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and chart a course toward success in the ever-evolving landscape of corporate governance and entrepreneurship.
Disclaimer: “This article is for educational & entertainment purposes.”

